Australia’s automotive landscape is rapidly evolving, with electric vehicles (EVs) at the forefront of the sustainability discussion. However, a new contender, e-fuels, also known as synthetic fuels, is emerging as a potential game-changer. These innovative fuels promise a carbon-neutral alternative to traditional fossil fuels, sparking debate: can e-fuels genuinely compete with EVs in the race for Australia’s sustainable transport future?
What exactly are e-fuels?
- E-fuels (also called synthetic fuels) are liquid or gaseous fuels produced by combining captured CO₂ and hydrogen derived via renewable electricity (electrolysis).
- They can often be used as “drop-in” replacements in internal combustion engine vehicles without major engine changes.
- Their appeal lies in compatibility with existing infrastructure (fuel pumps, vehicles) and the promise of a lower carbon footprint, provided the electricity is renewable.
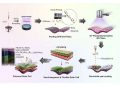
The key production steps include:
- Electrolysis of water → hydrogen
- Carbon capture (direct air or industrial) → CO₂
- Synthesis (e.g., Fischer-Tropsch) → hydrocarbon fuel

E-fuels are a class of synthetic fuels produced using renewable electricity. The core process involves extracting hydrogen from water through electrolysis and capturing carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere or industrial sources. These two elements are then combined in a chemical reaction to produce liquid fuels such as synthetic petrol, diesel, and even jet fuel.
Essentially, e-fuels offer a “drop-in” solution, meaning they can be used in existing internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and infrastructure. This characteristic is a significant advantage, offering a pathway to decarbonisation without requiring a complete overhaul of our current vehicle fleet.
The Australian context: Why e-fuels matter
- Australia is heavily reliant on imported liquid fuels, with refining capacity shrinking; this creates a domestic opportunity for low-carbon liquid fuels in hard-to-electrify sectors.
- But despite potential, there are currently few large-scale e-fuel projects in Australia compared to Europe.
- The research organisation, the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), is actively working on synthetic fuels in Perth, indicating that Australia is positioning for this new industry.
- The government and industry acknowledge this: Australia’s abundant solar and wind resources make it an attractive location for e-fuel production.
Going solar with confidence
Energy Matters is here to guide you every step of the way. We help Australian home and business owners receive personalised solar quotes through our large network of high-quality solar installers. We only work with reputable solar companies that have a proven track record of delivering high-quality solar systems.
E-fuels vs. EVs: A head-to-head comparison
The debate between e-fuels and EVs in Australia is multifaceted, encompassing efficiency, infrastructure, and environmental impact.
Efficiency:
- EVs: Electric vehicles are inherently more energy-efficient. A significant portion of the renewable electricity generated is used to power the wheels, with minimal energy loss.
- E-fuels: The production of e-fuels involves multiple energy conversion steps, resulting in significant energy losses. From electricity to hydrogen, then to synthetic fuel, and finally to propulsion in an ICE vehicle, the overall “well-to-wheel” efficiency is significantly lower than that of EVs. Estimates suggest that e-fuel production and use are 2-3 times less efficient than direct EV charging.
Infrastructure:
- EVs: Require a robust charging infrastructure, including public charging stations and home charging solutions. Australia is steadily building this out (see our guide on EV charging solutions for your home).
- E-fuels: Can leverage existing fuel distribution networks and refuelling stations. This “drop-in” capability is a major selling point because it avoids the massive investment required for new infrastructure.
Environmental Impact:
- EVs: Zero tailpipe emissions. The overall environmental impact depends on the source of electricity used for charging. When powered by renewable energy, EVs have the lowest lifecycle emissions.
- E-fuels: Offer “net-zero” carbon emissions from a lifecycle perspective, as the CO₂ released during combustion is captured during production. However, other pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), can still be emitted by ICE vehicles using e-fuels, though these emissions are generally lower than with traditional fossil fuels.
Will e-fuels compete with EVs in Australia? This table summarises key differences:
| Factor | Advantage for E-fuels | Advantage for EVs |
| Vehicle compatibility | Works with existing ICE vehicles, minimal change required | Offers new vehicle architecture, designed for EVs |
| Infrastructure | Uses existing fuel stations | Requires new charging infrastructure (growing rapidly) |
| Efficiency | Lower overall efficiency due to many conversion steps | High efficiency, fewer energy losses |
| Cost | Currently, the high cost of production and limited commercial scale in Australia | EV manufacturing costs decreasing, battery tech improving |
| Market focus | Applicable for hard-to-electrify sectors (heavy vehicles, aviation, classic cars) | Ideal for passenger transport where grid/charging access exists |
| Australian resource potential | A strong renewable resource base means Australia could become an exporter of synthetic fuels | Strong domestic market growth, local manufacturing potential for EVs |
Where e-fuels make most sense (and where they don’t)
Best use cases for e-fuels
- In sectors where battery-electric power is impractical (long-haul freight, certain aviation, and shipping), synthetic fuels have a strong role.
- In Australia, the production of e-fuels can serve export markets as well as transitional domestic use.
- For the large existing ICE vehicle fleet, e-fuels may offer a lower-carbon path before full electrification.
Where EVs remain dominant
- Typical passenger vehicles with good grid access and home charging infrastructure.
- Urban commuting, where “plug in and go” is more convenient than liquid fuel logistics.
- Instances where the highest energy efficiency and lowest long-term cost matter most.
Powering up your EV with solar
If you’re thinking of buying an EV, adding an EV charger to your solar system is a smart way to “fuel” your car with clean, renewable energy.
Key challenges facing E-fuels in Australia
- High production costs: Synthetic fuels remain expensive and technologically immature for large-scale deployment in road vehicles.
- Energy intensity: The conversion chain for synthetic fuels uses a lot of electricity—if that electricity isn’t truly renewable, the carbon benefit shrinks.
- Scale and timing: Australia’s e-fuel project pipeline is smaller than in other jurisdictions, suggesting widespread adoption may take time.
- Market overlap: As EVs scale, the window for synthetic fuels in passenger vehicles may shrink — meaning e-fuels might end up more niche than mainstream.
Sources: CSIRO – Meet the researchers fueling the future of synthetic fuels | MDPI – Overview of the e-Fuels Market, Projects, and the State of the Art of Production Facilities | CleanEnergy | Sustainable Aviation Future – Australia Looks to Sustainable Fuels to Secure Energy Future: Government and industry are working together to build Australia’s low carbon liquid fuel industry
The bottom line
While e-fuels Australia and synthetic fuels have exciting potential, especially for industrial and hard-to-electrify transport, they are unlikely to directly compete with EVs for mainstream passenger transport in Australia in the near term. For most drivers, EVs will continue to deliver the most significant benefit now.
EVs remain more efficient, increasingly affordable, and supported by growing infrastructure. For businesses and sectors facing unique challenges, e-fuels may provide a critical bridge. That said, e-fuels will play a valuable complementary role — especially in niche sectors and as part of Australia’s decarbonisation strategy.
Ready to dive deeper into your transport energy options? Visit Energy Matters for tailored analysis, or talk with our solar experts about how solar, EV charging, and low-carbon fuels can work for your home or business.